bsd/ospf | bsd/ospf-n-bgp | bsd/bgp | cisco/ospf | cisco/ospf-n-bgp | cisco/bgp

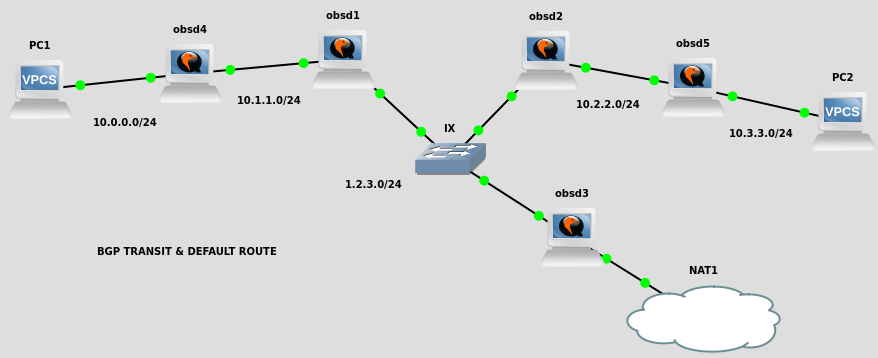
Here we have five BGP nodes, all doing transit between peers, and obsd3 announcing a default route instead.
vpcs*
ip 10.0.0.1/24 10.0.0.254 ip 10.3.3.1/24 10.3.3.254 save
workstation (libvirt)
no need for static routes because we’re doing NAT within the PoC (on obsd3)
obsd*
hostname obsd1
hostname obsd2
hostname obsd3
hostname obsd4
hostname obsd5
vi /etc/myname
obsd1
obsd2
obsd3
obsd4
obsd5
vi /etc/hostname.vio0
inet 1.2.3.1/24
inet 1.2.3.2/24
inet 1.2.3.3/24
inet 10.1.1.1/24
inet 10.2.2.1/24
vi /etc/hostname.vio1
inet 10.1.1.245/24
inet 10.2.2.254/24
dhcp
inet 10.0.0.254/24
inet 10.3.3.254/24
rm -f /etc/mygate
sh /etc/netstart
sysctl net.inet.ip.forwarding=1
sysctl net.inet6.ip6.forwarding=1
echo net.inet.ip.forwarding=1 >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo net.inet6.ip6.forwarding=1 >> /etc/sysctl.conf
vi /etc/bgpd.conf
AS 65001
AS 65002
AS 65003
AS 65004
AS 65005
router-id 1.2.3.1
router-id 1.2.3.2
router-id 1.2.3.3
router-id 10.1.1.1
router-id 10.2.2.1
connect-retry 30
log updates
network inet connected
neighbor 1.2.3.1 {
remote-as 65001
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 10.1.1.254 {
remote-as 65001
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 1.2.3.2 {
remote-as 65002
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 10.2.2.254 {
remote-as 65002
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 1.2.3.3 {
remote-as 65003
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 10.1.1.1 {
remote-as 65004
announce IPv4
}
neighbor 10.2.2.1 {
remote-as 65005
announce IPv4
}
allow from any
allow to any
bgpd -nf /etc/bgpd.conf
rcctl enable bgpd
rcctl restart bgpd
bgpctl show
bgpctl show rib
obsd3 only
vi /etc/bgpd.conf network inet connected network 0/0 mv /etc/pf.conf /etc/pf.conf.dist vi /etc/pf.conf pass out on vio1 from 10.0.0.0/24 to any nat-to (vio1) pass out on vio1 from 10.1.1.0/24 to any nat-to (vio1) pass out on vio1 from 10.2.2.0/24 to any nat-to (vio1) pass out on vio1 from 10.3.3.0/24 to any nat-to (vio1) pass out on vio1 from 1.2.3.0/24 to any nat-to (vio1) pfctl -nf /etc/pf.conf pfctl -f /etc/pf.conf
vpcs1
ping 10.3.3.1 trace 10.3.3.1 ping 192.168.122.1 trace 192.168.122.1 ping 1.1.1.1 trace 1.1.1.1
vpcs2
ping 192.168.122.1 trace 192.168.122.1 ping 1.1.1.1 trace 1.1.1.1
# Martians IPv4 deny from any prefix 0.0.0.0/8 prefixlen >= 8 deny from any prefix 127.0.0.0/8 prefixlen >= 8 deny from any prefix 169.254.0.0/16 prefixlen >= 16 deny from any prefix 198.18.0.0/15 prefixlen >= 15 # Martians IPv6 deny from any prefix ::1/128 deny from any prefix ::/128 deny from any prefix ::ffff:0:0/96 prefixlen >= 96 deny from any prefix 64:ff9b::/96 prefixlen >= 96 # Filtering too specific prefixes deny from any inet prefixlen > 24 # Default route filtering deny from any inet prefix 0.0.0.0/0 prefixlen = 0 deny from any inet6 prefix ::/0 prefixlen = 0 # AS_PATH filtering enforce neighbor-as yes
BGP https://securityrouter.org/wiki/BGP
OpenBGPD https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenBGPD
OpenBGPD (∞) https://why-openbsd.rocks/fact/openbgpd/
bgpd.conf — Border Gateway Protocol daemon configuration file https://man.openbsd.org/bgpd.conf.5
IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack BGP Configuration: Part 1 – OpenBGPD http://mindless.gr/2011/07/dual_stack_bgp_configuration_openbgpd/
Configuring BGP on Vultr With OpenBSD https://www.vultr.com/docs/configuring-bgp-on-vultr-with-openbsd
Routing with bgpd https://web.archive.org/web/20200118022955/https://www.nomoa.com/bsd/gateway/routing/bgp.html
https://labs.ripe.net/author/claudio_jeker/openbgpd-adding-diversity-to-the-route-server-landscape/
https://www.openbsd.org/faq/upgrade64.html
https://cvsweb.openbsd.org/cgi-bin/cvsweb/src/usr.sbin/bgpd/parse.y#rev1.322
OpenBSD OpenBGPD Notes https://www.packetmischief.ca/openbsd-openbgpd-notes/
BGP configuration best practices https://www.ssi.gouv.fr/uploads/2016/03/bgp-configuration-best-practices.pdf
bgpq4 - bgp filtering automation tool https://github.com/bgp/bgpq4
Route Server https://web.archive.org/web/20200201202749/https://bgp-spamd.net/routeserver/bgpd.html
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/white_paper_c11-516826.html
OpenBGPd and route filters http://undeadly.org/cgi?action=article&sid=20151106171337&mode=expanded
High Availability With OpenBGPD on OpenBSD 6.9 https://kernelpanic.life/software/high-availability-with-openbgpd-on-openbsd.html
https://ogris.de/howtos/openbsd-looking-glass.html
https://dn42.eu/howto/OpenBGPD
https://www.knowledgebombs.net/blog/2012/12/13/bgplg-from-scratch.html
(4.8) OpenBGPd sometimes does not send the routes to the peer. https://misc.openbsd.narkive.com/KcIFBPHm/4-8-openbgpd-sometimes-does-not-send-the-routes-to-the-peer
OpenBSD: Defining a new loopback interface https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/371025/openbsd-defining-a-new-loopback-interface
Dummy Interface In OpenBGPd https://misc.openbsd.narkive.com/Xon0No5m/dummy-interface-in-openbgpd
OpenBGPD: Announce all problem and strange rib-out entries. https://misc.openbsd.narkive.com/B4Y3DTlX/openbgpd-announce-all-problem-and-strange-rib-out-entries
The BIRD IRD https://bird.network.cz/
OpenBGPD: The OpenBSD BGP internet routing daemon (openbgpd.org) https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=20540871
List of open-source routing platforms https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_open-source_routing_platforms