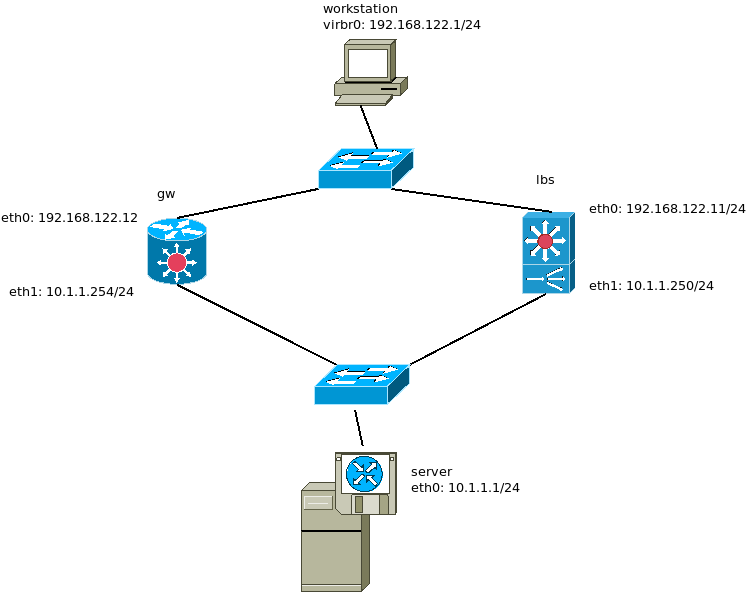

problem is that our mangling now prevents outbound connections to work from server because it interferes with any casual snat rule. (most probably because mangling priority is simply higher than srcnat priority)
for exemple adding casual SNAT back in the game
# try catch UDP and TCP SYN as usual and with states
table ip nat {
# SNAT
chain postrouting {
type nat hook postrouting priority srcnat;
oif eth0 ip saddr 10.1.1.0/24 snat 192.168.122.11;
}
}
# catch everything
(diy-snat-spoof from part2 here)
doesn’t help
from server
ping -c1 192.168.122.1 -W1
==> 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 0ms
ping -c1 192.168.122.1 -W1
==> 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 0ms
as seen while sniffing eth0 on gw, spoofing is in action
# tcpdump -ni eth0 not tcp port 22 04:27:11.841533 IP 192.168.122.12 > 192.168.122.1: ICMP echo request, id 907, seq 1, length 64
so let’s attempt to tag/mark the dataframes on the way in, so we know what kind of flow we’re talking on the outbound gw. also this would ideally help extend the current PoC to a full-blown cluster setup with different inbound IPs.
choose a diffserv code to probe with
nft describe ip dscp # here cs1 (0x08)
enhance the diy-dnat rules with it
table ip diy-dnat {
chain prerouting {
type filter hook prerouting priority mangle;
iif eth0 tcp dport 80 notrack ip daddr set 10.1.1.1 ip dscp set cs1
iif eth0 tcp dport 1234 notrack ip daddr set 10.1.1.1 ip dscp set cs1
iif eth0 udp dport 1234 notrack ip daddr set 10.1.1.1 ip dscp set cs1
iif eth0 tcp dport 2201 notrack ip daddr set 10.1.1.1 tcp dport set 22 ip dscp set cs1
}
}
and check there’s DiffServ in da place – sniffing the link between lbs and server with wireshard – tcpdump isn’t quite appropriate for that one
from the workstation
curl -I 192.168.122.12 ssh 192.168.122.12 -l root -p 2201
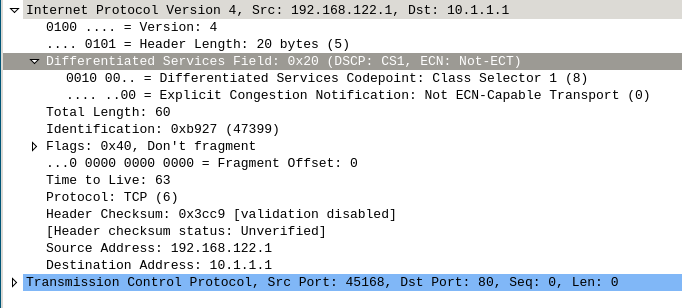
==> shows up as DiffServ 0x20
but if you really want to stick with tcpdump, you might as well catch it while sniffing the internal interface on lbs
tcpdump -ni eth1 '(ip and ip[1] & 0xfc == 0x20)' -v
now the problem is, the tag gets lost on the server, while bouncing back to gw
==> DiffServ 0x00 / CS0
for that purpose, let us keep track of the QoS tag through connection tracking on the server side
flush ruleset
table inet mangle {
chain prerouting {
type filter hook prerouting priority -150;
iif eth0 ip dscp != 0 ct mark set 0x01
}
chain postrouting {
type filter hook postrouting priority 150;
oif eth0 ct mark != 0 ip dscp set cs1
}
}
check that you’re seeing DiffServer 0x20 yet again on the link between the server and the outbound gateway
from the workstation
curl -I 192.168.122.12 ssh 192.168.122.12 -l root -p 2201
==> yes, the mangling trick occured on the server side
now on the outbound gateway, apply diy-snat-spoof only for DiffServ tagged packets – so that the casual SNAT can live in peace – and clean-up the tag at once
flush ruleset
# catch outbound and non-tagged flows
table ip nat {
# SNAT
chain postrouting {
type nat hook postrouting priority srcnat;
oif eth0 ip saddr 10.1.1.0/24 snat 192.168.122.11;
}
}
# catch tagged flows and reverse the stateless port-forwarding
table ip diy-snat-spoof {
chain postrouting {
type filter hook postrouting priority mangle;
oif eth0 ip saddr 10.1.1.1/32 tcp sport 22 tcp sport set 2201
oif eth0 ip saddr 10.1.1.0/24 ip dscp cs1 notrack ip saddr set 192.168.122.12 ip dscp set cs0
}
}
check for an outbound connection again from server
ping 192.168.122.1 -c3 -W1
==> 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
while sniffing the external interface on the outbound gw
tcpdump -ni eth0 not tcp port 22
==> all good, no spoofing required on that one
16:53:16.607672 IP 192.168.122.11 > 192.168.122.1: ICMP echo request, id 1304, seq 1, length 64 16:53:16.608507 IP 192.168.122.1 > 192.168.122.11: ICMP echo reply, id 1304, seq 1, length 64